반응형
- 객체 지향 프로그래밍
특징
- 캡슐화, 상속, 다형성, 추상화
- 클래스의 구성 멤버
- 필드, 생성자, 메소드
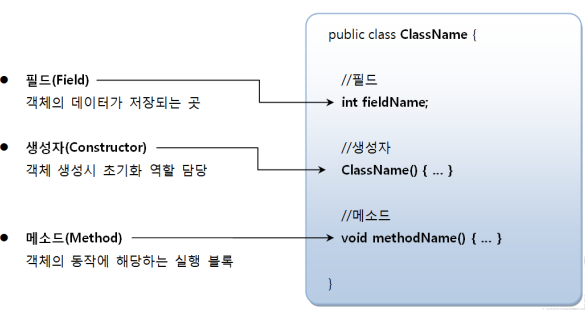
- 필드
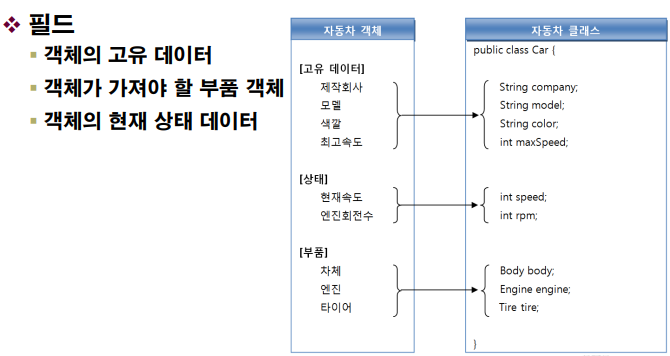
- 필드
public class Car {
String company;
String model;
int maxSpeed;
void setInfo(String c, String m, int ms) {
company = c;
model = m;
maxSpeed = ms;
}
void printInfo() {
System.out.println("제조사 : " + company);
System.out.println("모델 : " + model);
System.out.println("최고속도 : " + maxSpeed);
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
public class CarDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new Car();
Car car2 = new Car();
// car1 객체 필드 값 설정
car1.company = "현대차";
car1.model = "제네시스";
car1.maxSpeed = 270;
car1.printInfo();
System.out.println();
// car2 객체 필드 값 설정
car2.company = "삼성";
car2.model = "QM5";
car2.maxSpeed = 300;
car2.printInfo();
System.out.println();
// static이 붙은 메소드는 ( 클래스명.메소드() )
// static이 없는 메소드는 ( 참조변수.메소드() )
// setInfo() 사용하여 생성
Car car3 = new Car();
car3.setInfo("테슬라", "모델S", 300); // 필드값 초기화
car3.printInfo();
}
}
- 생성자

- 기본생성자
▪ 생성자 선언을 생략한 경우 컴파일러는 기본생성자를 추가한다.
▪ 컴파일러가 추가한 생성자의 접근제한자는 클래스의 접근제한자를 따른다.
public class Car {
String company;
String model;
int maxSpeed;
}
// 컴파일러가 자동으로 생성자를 넣어주는 코드
public class CarDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new Car();
}
}
- 생성자를 추가한 경우
▪ 다른 생성자가 존재하는 경우 기본생성자를 직접 추가하여 사용해야 한다.
public class Car {
String company;
String model;
int maxSpeed;
public Car() {
// 기본 생성자
}
// 기본 생성자가 아닌 다른 생성자가 정의 되어있다면
// 기본 생성자를 생략할 수 없다.
// 다른 생성자란 매개변수를 가지는 생성자를 말한다.
// 매개변수가 있는 생성자
public Car(String c, String m, int ms) {
company = c;
model = m;
maxSpeed = ms;
}
}
public class CarDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new Car();
Car car2 = new Car("현대", "K5", 400);
}
}
- 필드 초기화
public class Korean {
String nation = "대한민국"; // 필드 선언시 초기화
String name;
String ssn;
public Korean(String name, String ssn) { // 생성자 초기화
this.name = name;
this.ssn = ssn;
}
void print() {
System.out.println("국적 : " + nation);
System.out.println("이름 : " + name);
System.out.println("주민번호 : " + ssn);
System.out.println();
}
}
public class KoreanExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Korean kor1 = new Korean("짱구", "112344-3564561");
Korean kor2 = new Korean("맹구", "991344-1564561");
kor1.print();
kor2.print();
}
}
- 생성자 오버로딩(Overloading)
- 매개변수의 타입, 개수, 순서가 다른 생성자 여러 개 선언
- 타입이 같은 매개변수의 순서를 바꾸는 것은 오버로딩이 아님
- 타입이 "다른" 매개변수의 순서를 바꾸는 것은 생성자 오버로딩이다
- 즉! 오버로딩은 매개변수 이름이 아닌, 타입으로 결정
public class Car {
String company;
String model;
String color;
int maxSpeed;
public Car() {}
public Car(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public Car(String model, String color) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
}
public Car(String model, String color, int maxSpeed) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.maxspeed = maxSpeed;
}
public Car(String model, int maxSpeed, String color) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.maxspeed = maxSpeed;
}
}
- 생성자 자동완성 단축키
shift + alt + s
Generate Constructor using field 선택
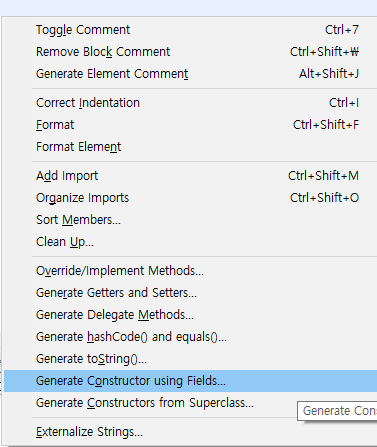
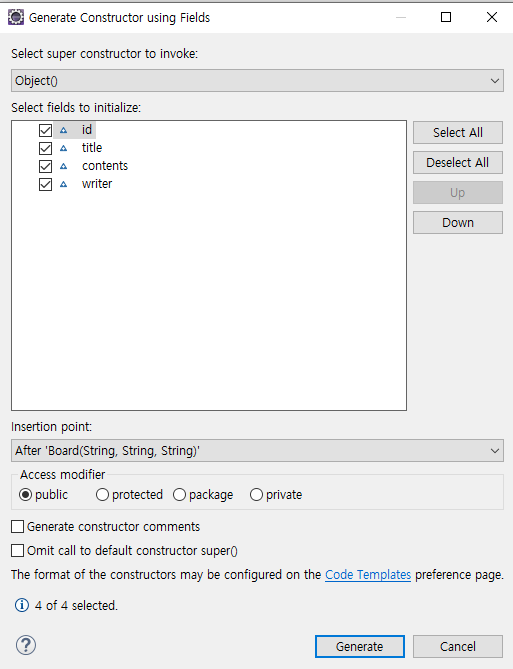
원하는 필드 체크후 아래쪽 Generate 클릭
- 다른 생성자 호출 (this())
- this()생성자는 반드시 생성자의 첫 줄에만 허용된다.
- 생성자 내에서 this()생성자 보다 앞선 다른 코드를 허용하지 않는다. (공백인 경우는 괜찮다.)
// 안되는 예제
public Car() {
System.out.println("기본생성자 실행");
this("포니");
}
// 되는 예제
public Car() {
this("포니");
System.out.println("기본생성자 실행");
}this()가 생성자 가장 첫 줄에 있지 않으면 컴파일 오류가 뜬다.
오류 문구: Constructor call must be the first statement in a constructor
반응형
'학습 > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. 클래스(정적(static), 인스턴스, 싱글톤(singleton), 상수, 접근 제한자, Getter & Setter (1) | 2022.10.07 |
|---|---|
| 6. 클래스(메소드, 인스턴스 멤버와 this) (0) | 2022.10.06 |
| 5. 열거 타입 (0) | 2022.10.05 |
| 5. 참조 타입 (0) | 2022.10.04 |
| 4. 반복문(for문, while문, do-while문 (0) | 2022.09.30 |




댓글